The phenomenal evolution of the Datacenter in the last decade

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
What are the expectations of the future data center? Are the data centers that are all about multi-racks of Servers, Storage, cables & cooling systems going through a transformation? What are the trends in Industry and Storage technology that are influencing the change?
Storage revolution in the early 90’s brought in rise of multibillion dollar Institutions such as EMC2, NetApp, etc. who came up with innovative and robust offerings that redefined the data centers to be storage specific instead of server specific. Features such as RAID, Hot spares etc. evolved from their DAS forms in to High availability, Migration etc. Novel ideas of Clones, Snapshots redefined data protection at the source. Deduplication and compression which were once considered desktop solutions expanded to redefined both primary and secondary storage (backup) appliances to the extend they schematically started replacing the traditional backup done through tape storage. And story went on FC, FCIP, FCoE, etc. replaced SCSI based simple systems, etc. Also, virtualization has started becoming a reality even in mission critical applications beyond being in the need of resource optimization or budgeting.
But the question remains, have we achieved the penultimate of how much storage can evolve? Are data centers going to be still storage dominant? What do the developments in cloud, big data, flash etc. mean to future data centers? This series of articles proposes to discuss the possibilities on such questions about a future data center but with reference to the traditional architecture’s evolution. Let’s first have a bird’s eye view of how data centers have evolved.
Evolution of Data Center Architecture:
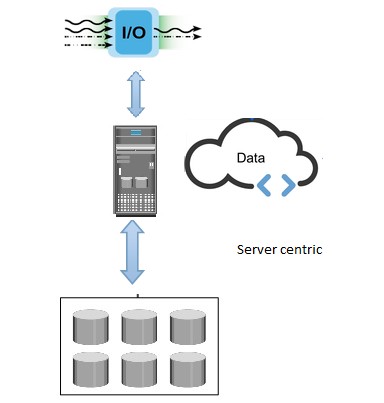
Server Centric Architecture:
Server centric data centers depended on the server’s capability to ensure business continuity. That defined the Server to be reliable to the extent that there are no component failures before MTBF (Mean time before failure), they are 24/7 available, supports scalability supporting the need of data & performance for about 5 years or so, upgradable features & components with/ without licenses & Manageable by standard Admin procedures. Companies such as AMI, Promise, Adaptec & LSI were Storage market leaders contributing to DAS scheme of products enabling the Application, Web or Database servers to store date with protection. The capabilities of Applications played a role complimentary to the capabilities of the Server architecture. The ‘Server Centric’ picture show below illustrates how the compute capabilities of Server determined the capability of the data center. The server centric architecture had its dependence on different RAID levels for data protection. Also, the Storage capability of a single system never grew beyond few terabytes of data. Intel, HP, IBM, Dell were major drivers of the evolution of Server systems and they still continue to be so.
Storage Centric Architecture:
Need for high availability of Storage and Networking Infrastructure in the mid 90’s initiated an era of storage dominant data center architecture. The business needs demanded continuous availability that did not permit downtime even for periodic upgrades. Seamless scalability and upgradability became norms. Infrastructure that did not support non-disruptive upgrades were no more considered relevant.
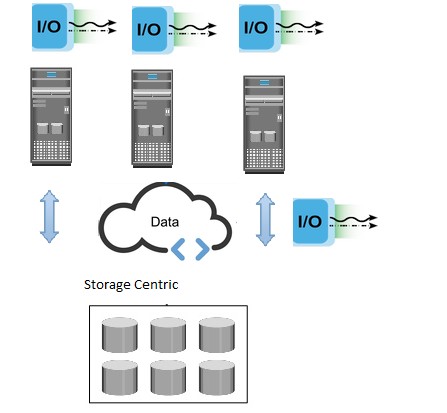
Storage efficiency and availability became the prime mover for customer’s needs. The appliance costs sky rocketed but the capability of the enterprise storage system grew to support always available production systems managing terabytes of data. SAN (Storage area Networks) brought together various organizations to help in consolidated development of integrated, interoperable storage infrastructure. Some companies pioneered the FC/ FCOE/iSCSI Host Bus Adapters that are the backbone of storage subsystems. The HBA logic were well enhanced to suit the highly available enterprise needs by companies such as EMC, NetApp, HP, IBM etc. who innovated large storage arrays with complex integration capabilities with various Server systems that run any application, any OS platform, any hardware can access one large enterprise storage facilitated by robust FC protocol methods such as zoning, masking, etc. designed on the FC/ FCoE, etc switches provided by CISCO, Brocade, McData, etc. The RAID levels/ data protection methods such as snap/ clone were integrated into the storage appliances based on server/ application needs instead of having them designed in servers (hosts). The HBA’s residing in Hosts/ Servers played the role of initiators, that of those who initiate an exchange with the targets (storage appliances) which are connected to the servers in highly available configuration exploiting the redundant switch systems.
Though SAN evolution predominantly meant the storage access is block based, the parallel evolution of NAS technology via CIFS, NFS protocols paved way for file based IO access too. And the NAS could be integrated into the SAN through Gateway appliances. Also, the storage majors propounded ideas of object oriented storage to facilitate application specific storage management. The migration features enabled the data to be moved across supported storage arrays and made the storage upgrades reliable and possible without downtime.
Most of the modern data centers are storage specific. However, with emergence of social media, robust and vastness of data needs, storage administrators are experiencing the limitations of vendor specific, appliance specific and not to mention the huge costs involved in expansion of storage and majorly the complexity of storage consolidation.
The Story Next?
The dawn of 21st century saw the emergence of a super power in the data centers who raised dominance in a decade’s time that checked the monopoly of dominance enjoyed by big storage players. They played an old card that was played a decade back by few companies including Apple Inc but not so successfully and when they did, that propelled a serious introspection on how we should be managing our data centers and bring in a steady Storage consolidation. For those who’ve guessed, yes, we are talking about an idea called ‘Virtualization’ reinvented by VMware.
